Skin Cancer Basics: Types, Symptoms, and Early Detection
Skin cancer is a significant health concern in Australia due to the country’s high levels of ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Understanding the basics of skin cancer, its types, symptoms, and early detection methods is crucial for everyone. This informative blog post aims to provide basic information to help raise awareness about skin cancer and promote early detection.
Main types of Skin Cancers
Melanoma
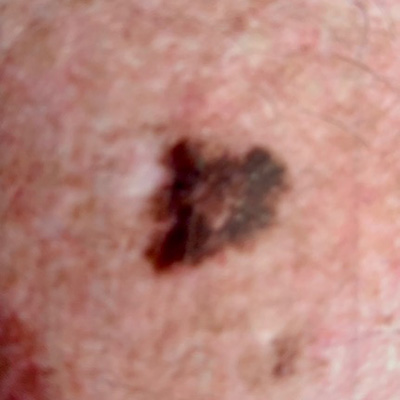
Melanoma is the most aggressive form of skin cancer. It originates in the cells that produce pigment, known as melanocytes. It can occur on any part of the body and often presents as a new or changing mole.
- Appearance: Melanoma often starts as an irregular, asymmetrical mole with uneven borders and a mix of colors (black, brown, blue, red, or white).
- Size: It can be larger than a pencil eraser (6mm), but can also begin as a smaller spot.
- Change: Melanomas can evolve, so any changes in size, color, shape, or elevation should be noted.
- Symptoms: It might itch, bleed, or become painful.
- Common Locations: Common areas include the back, legs, arms, face, and chest.
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
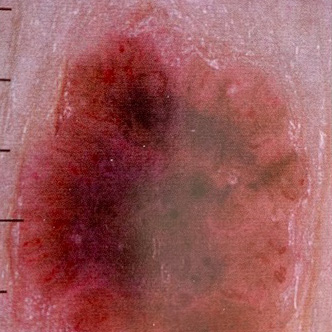
BCC is the most common type of skin cancer. It typically appears as a raised, pearly bump or a sore that doesn’t heal. While it tends to grow slowly and rarely spreads to other parts of the body, early detection is still important.
- Appearance: BCC often appears as a raised, pearly bump or a waxy, pinkish patch.
- Blood Vessels: It might have visible blood vessels on the surface.
- Ulceration: It can ulcerate or form a crust, with a center that oozes or bleeds.
- Slow Growth: BCC grows slowly and might resemble a scar-like lesion.
- Common Locations: Face, head, and neck are common sites.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
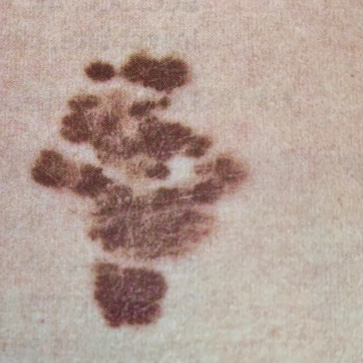
SCC is another common type of skin cancer. It often appears as a scaly, red patch, an open sore, or a raised growth with a central depression. SCC can spread to other parts of the body if not treated promptly.
- Appearance: SCC frequently appears as a scaly, red patch or a rough, thickened bump.
- Ulceration: It can ulcerate, form a crust, or develop into an open sore.
- Growth: SCC might grow rapidly and be painful.
- Elevation: The bump might be elevated, firm, and tender.
- Common Locations: Head, neck, ears, lips, and hands are often affected.
Common Symptoms to watch For
- Changes in Moles: Keep an eye on any moles or growths that change in size, shape, color, or texture.
- New Spots: Be cautious of new spots that appear on your skin, especially if they are dark, irregular, or growing.
- Sores that Don’t Heal: Non-healing sores, ulcers, or lesions that persist for weeks can be a sign of skin cancer.
- Scaly or Crusty Patches: These patches might bleed, ooze, or become inflamed.
- Itchy or Painful Lesions: Any lesions that become itchy, tender, or painful should be examined by a medical professional.
Early intervention can greatly impact successful outcomes and ensure your skin health. It’s important to note that these descriptions are general guidelines, and any suspicious changes on your skin should be examined by a medical professional. Regular self-examinations and professional skin checks are essential for early detection and effective treatment. If you notice any concerning changes, seek medical advice promptly.
Early Detection and Prevention
Early detection is key to successful treatment. Here’s what you can do:
- Regular Self-Examination: Perform a monthly self-skin examination to monitor any changes in your skin.
- Sun Protection: Protect your skin from harmful UV rays by wearing protective clothing, hats, sunglasses, and using broad-spectrum sunscreen.
- Seek Professional Help: If you notice any concerning changes in your skin, consult a dermatologist or a medical professional for a thorough examination.
- Professional Skin Checks: Consider regular professional skin checks, especially if you have a history of sun exposure or a family history of skin cancer.
Conclusion
Skin cancer is a serious health issue, but with awareness and early detection, it is highly treatable. Understanding the types, symptoms, and early detection methods is essential for maintaining healthy skin. If you have any concerns about your skin health, don’t hesitate to reach out to a dermatologist or medical professional for proper evaluation and guidance. Remember, prevention and early detection are your best defenses against skin cancer.
