Home » Patient Information » Skin Cancer Types
Skin Cancer Types
Skin cancer is the most common form of cancer in Australia. Skin cancer is a disease of the body’s skin cells caused mainly by cumulative exposure to ultraviolet radiation (UVR) from the sun.
Cancer is a group of diseases in which cells are aggressive (grow and divide without respect to normal limits), invasive (invade and destroy adjacent tissues), and sometimes metastatic (spread to other locations in the body).
There are 3 types of skin cancer and they are named after the type of skin cell they originate from.
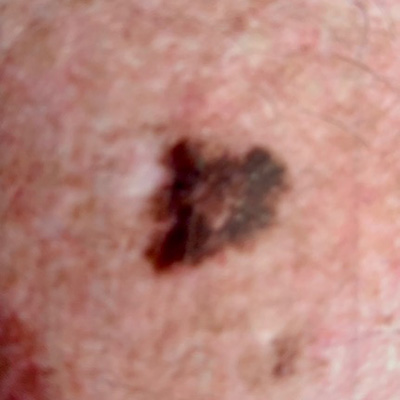
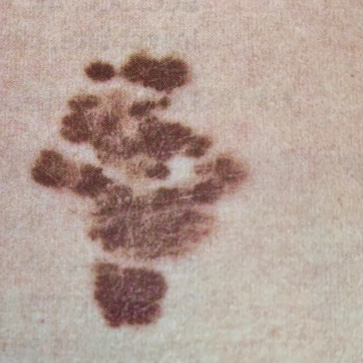
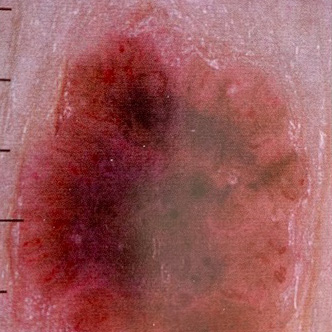
1. Melanoma skin cancer
- The least common but most serious form of skin cancer.
- Can appear in a new or an existing spot, freckle or mole that changes colour, size or shape.
- May have an irregular shape and be more than one colour
- Can sometimes be itch or bleed
- Grows anywhere on the body but most common on the back, legs, arms and face
If untreated, cancer cells can metastasise (spread to other locations of the body).
2. Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)
- Less common, but more dangerous than basal cell carcinoma.
- 1 to 2 percent can spread and cause death.
- Look for scaly red areas that may bleed easily, ulcers or non-healing sores that are often painful.
- Grows over a period of months.
- Often found on lips, ears, and scalp.
3. Basal cell carcinoma(BCC)
- The most common form of skin cancer but the least dangerous.
- Appear as round or flattened lump or scaly spots.
- Red, pale or pearly in colour.
- May become ulcerated, bleed and fail to heal.
- Grows slowly.
- Usually found on the upper body, head or neck.
SCC and BCC are also known as non-melanoma skin cancer or keratinocyte cancers.
The warning signs of Sun Damage to Your Skin
The following conditions are not cancer but may predispose you to skin cancer or be a warning sign that damage to the skin or eyes has occurred.
Dysplastic naevi:
- Are odd-shaped (also called atypical) moles that aren’t cancer, but may indicate a greater risk of developing melanoma.
- Usually 5 to 10mm wide, with uneven colouring.
If you have lots of odd-shaped moles you are at a higher risk of developing skin cancer and should have your skin checked regularly by your doctor
Solar Keratosis:
- Generally, hard, red, scaly spots on sun-exposed areas of the skin.
- Occur commonly on the head, neck and the backs of the hands.
Are a warning sign that the skin has been damaged by the sun and that skin cancer may develop.

- 268 Ipswich Road, Annerley QLD 4103
- 07 3891 3044
- Monday to Friday - 9.00 am – 5:00 pm
Weekends and Public Holidays - Closed
- Shop 1096C/1151 Creek Road, Carindale QLD 4152
- 07 3892 1985
- Monday to Friday - 9.00 am – 5:00 pm
- Note : Clinic is located on the outer part of the shopping center next to the CBA & ANZ bank, please take the Aldi/Big W entrance to the shopping center off Creek rd.
- 262 Old Cleveland Road, Coorparoo QLD 4151
- 07 3397 1999
- Monday to Friday - 8.00 am – 5:00 pm
Thursday : Late night appointments available till 6.00 pm
Saturday: 8.00 am -2.00 pm
Sunday and Public Holidays - Closed
No referral needed
Open Saturdays, early morning and late evenings
